Ever wished you could talk to your Kafka cluster using natural language—or call it directly from Claude Desktop or any other LLM client? With Model Context Protocol (MCP) and the FastMCP SDK, you can expose all your Kafka operations as discrete, promptable tools.
In this guide you’ll learn how to setup a MCP server to do the following:
- List Kafka topics
- Create & delete topics
- Produce messages
- Troubleshoot issues via a free‑form prompt
Try it out & contribute: GitHub Repo
Project Setup
git clone https://github.com/joel-hanson/kafka-mcp-server.git
cd kafka-mcp-server
# Create environment
conda create -n kafka-mcp python=3.10 -y
conda activate kafka-mcp
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Requirements:
- Python 3.10+
- A running Kafka broker (e.g.
localhost:9092; you candocker compose upa quick cluster) - MCP CLI tools (
mcp[cli]) andkafka-python - Optional: Claude Desktop or any MCP‑compatible LLM client
File Structure
kafka-mcp-server/
├── server.py # FastMCP entrypoint: registers @tool, @resource, @prompt
├── kafka_utils.py # Connection loader & reusable KafkaManager
├── kafka_troubleshoot.py # Static troubleshooting guide constant
├── requirements.txt
└── README.md
server.py– your main MCP server. Decorate functions with@mcp.tool()for command‑style operations,@mcp.resource()for raw JSON endpoints,@mcp.prompt()for free‑form guidance.
kafka_utils.py– handles parsingkafka.properties, instantiates and caches your KafkaAdminClient/Producer/Consumer, and stores it onlifespan_context.kafka_manager.– contains
KAFKA_TROUBLESHOOTING_GUIDE, a templated Markdown guide you plug into your@prompt().
Defining Your Tools
1. Initialize & Connect
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Kafka MCP Server", lifespan=kafka_lifespan)
@mcp.tool()
def kafka_initialize_connection(path: str) -> str:
"""Load kafka.properties and connect to the cluster."""
try:
manager = KafkaManager.from_properties(path)
ctx.request_context.lifespan_context.kafka_manager = manager
return "Connected to Kafka cluster."
except Exception as e:
return f"Connection failed: {e}"
2. List Topics (rich example)
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Kafka MCP Server", lifespan=kafka_lifespan)
@mcp.tool()
def kafka_list_topics(ctx: Context) -> str:
"""List all topics in the Kafka cluster"""
manager = ctx.request_context.lifespan_context.kafka_manager
if not manager:
return "Error: Not connected. Use kafka_initialize_connection first."
try:
topics = manager.list_topics()
if not topics:
return "No topics found in the Kafka cluster."
lines = [
f"• {t['name']} (partitions: {t['partitions']}, replication: {t['replication_factor']})"
for t in topics
]
return "Topics in Kafka cluster:\n" + "\n".join(lines)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error listing topics: {e}"
3. Raw JSON Resource
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Kafka MCP Server", lifespan=kafka_lifespan)
@mcp.resource("kafka://topics")
def get_all_topics() -> str:
"""Provide all Kafka topics as JSON"""
manager = mcp.get_context().request_context.lifespan_context.kafka_manager
if not manager:
return "Not connected to Kafka cluster"
try:
return json.dumps(manager.list_topics(), indent=2)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error fetching topics: {e}"
4. Troubleshooting Prompt
from kafka_troubleshoot import KAFKA_TROUBLESHOOTING_GUIDE
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Kafka MCP Server", lifespan=kafka_lifespan)
@mcp.prompt()
def kafka_troubleshoot(issue: str) -> str:
"""Get comprehensive troubleshooting guidance for Kafka issues"""
return KAFKA_TROUBLESHOOTING_GUIDE.format(issue=issue)
5. (Bonus) Produce
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Kafka MCP Server", lifespan=kafka_lifespan)
@mcp.tool()
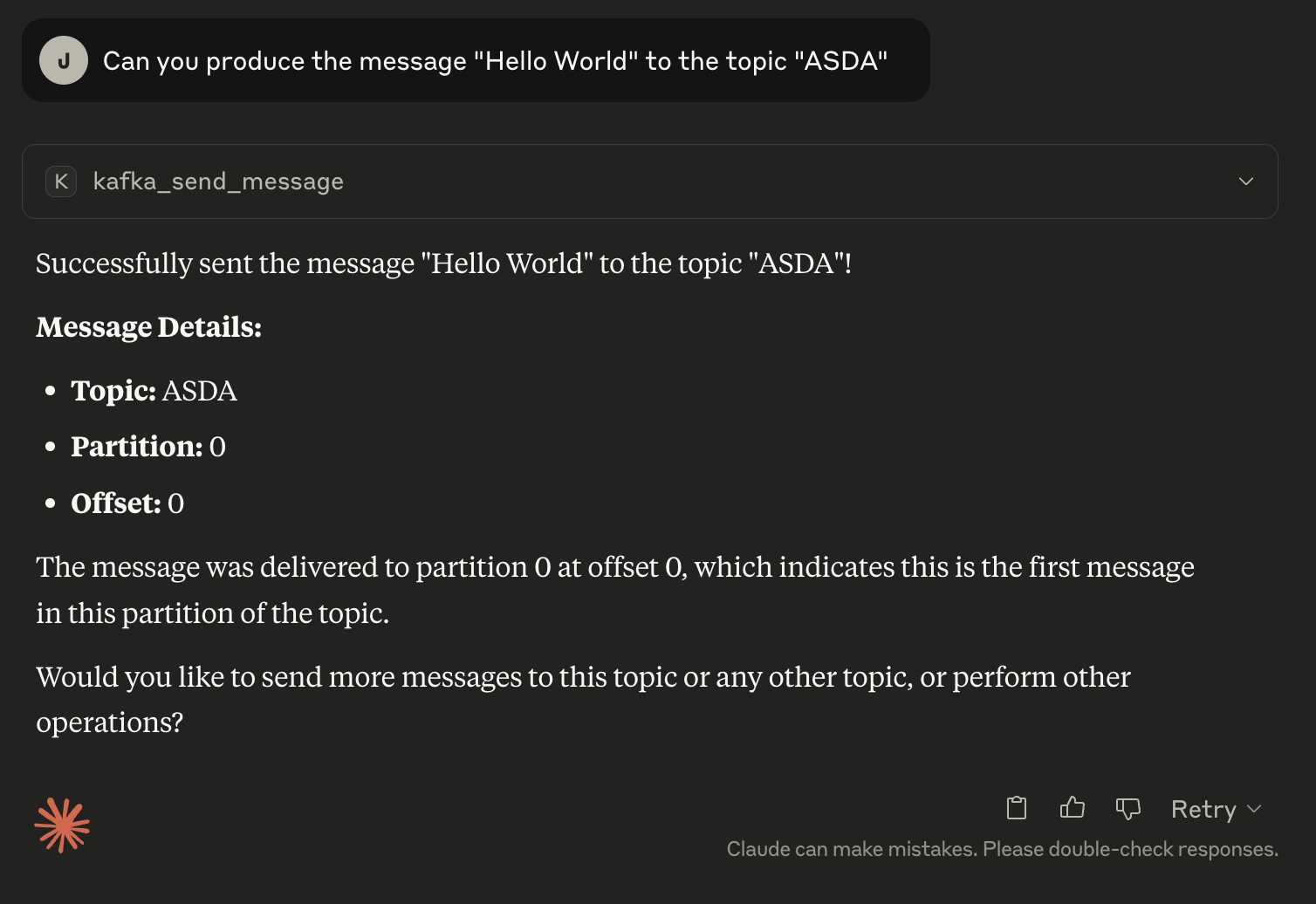
def kafka_produce(topic: str, message: str) -> str:
"""Send a message to a Kafka topic"""
prod = ctx.request_context.lifespan_context.kafka_manager.producer
try:
prod.send(topic, message.encode('utf-8'))
prod.flush()
return f"Message sent to `{topic}`: {message}"
except Exception as e:
return f"Error producing message: {e}"
Quick Start
1. Clone & Set Up
git clone https://github.com/joel-hanson/kafka-mcp-server.git
cd kafka-mcp-server
conda create -n kafka-mcp python=3.10 -y
conda activate kafka-mcp
pip install -r requirements.txt
2. Start Kafka with Docker (Recommended)
Before running your MCP server, bring up a local Kafka cluster:
docker compose up -d
This starts a Kafka broker on localhost:9092. You can now use the kafka.properties file to connect.
bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092
client.id=kafka-mcp-client
3. Running the MCP Server
Option 1: Dev mode with Inspector (Recommended)
mcp dev server.py
This launches the server with the MCP Inspector, a GUI for exploring tools and prompts.
Option 2: Headless
python server.py
Sprinkle logging.debug(...) in your tool functions to trace errors in real time.
Why use Docker Compose? It gives you a reliable, reproducible Kafka environment for local development—no need to install Kafka manually.
Example Usage Flow
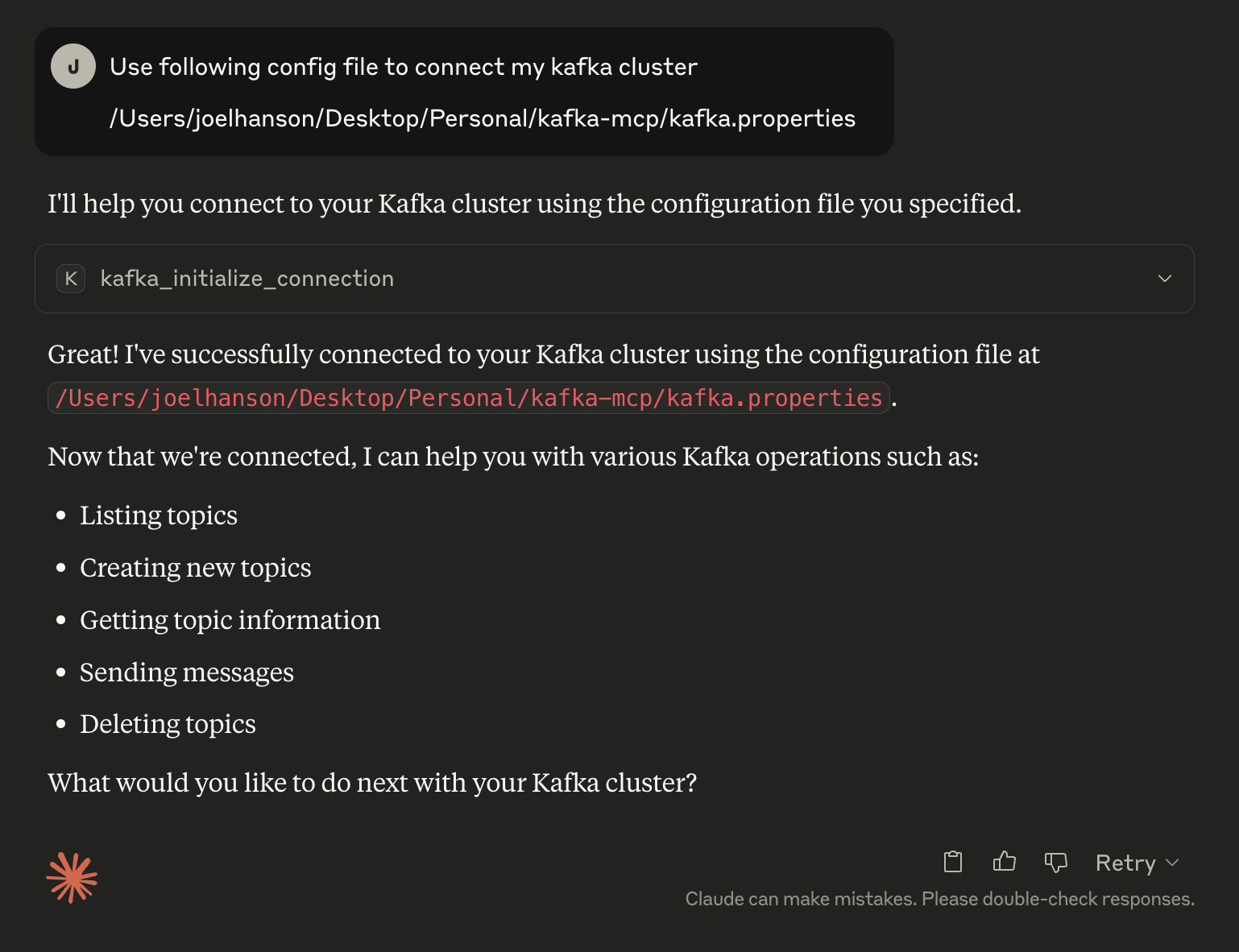
First, connect to Kafka:
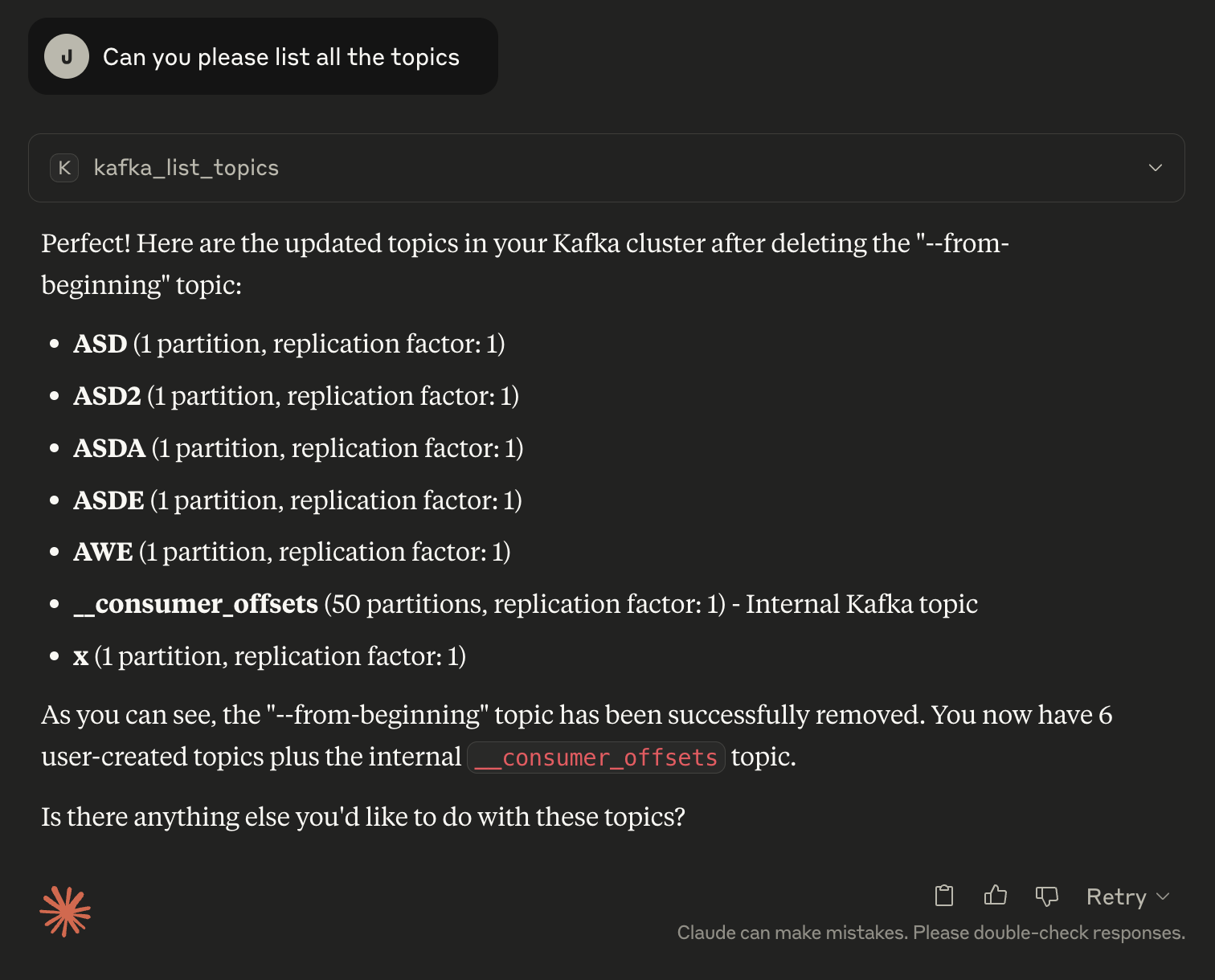
Use kafka_initialize_connection with your properties file <path> OR Initialize connection with kafka using the properties file <path>List existing topics:
Use kafka_list_topics to see all topics OR List all the topicsCreate a new topic:
Use kafka_create_topic with name "my-topic", partitions 3, replication_factor 1 OR Create me a topic with name "my-topic"Get topic details:
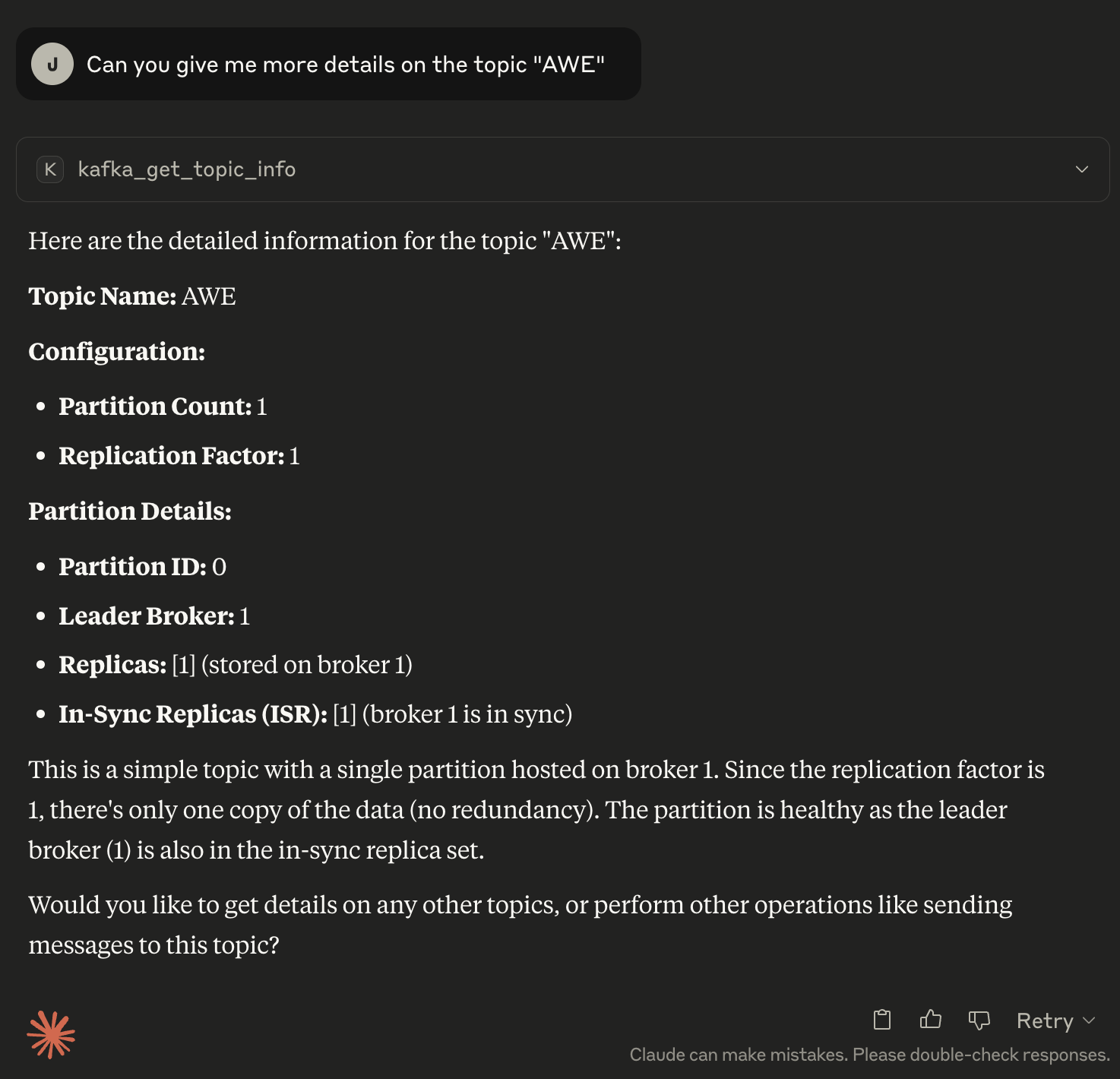
Use kafka_get_topic_info for "my-topic" OR Please share the topics details of "my-topics"
Integrating with Claude Desktop
Configure claude_desktop_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"Kafka MCP Server": {
"command": "/opt/miniconda3/envs/kafka-mcp/bin/python",
"args": ["server.py"]
}
}
}
Now Claude will auto‑discover and surface your new Kafka tools.
Screenshots
1. Listing available tools
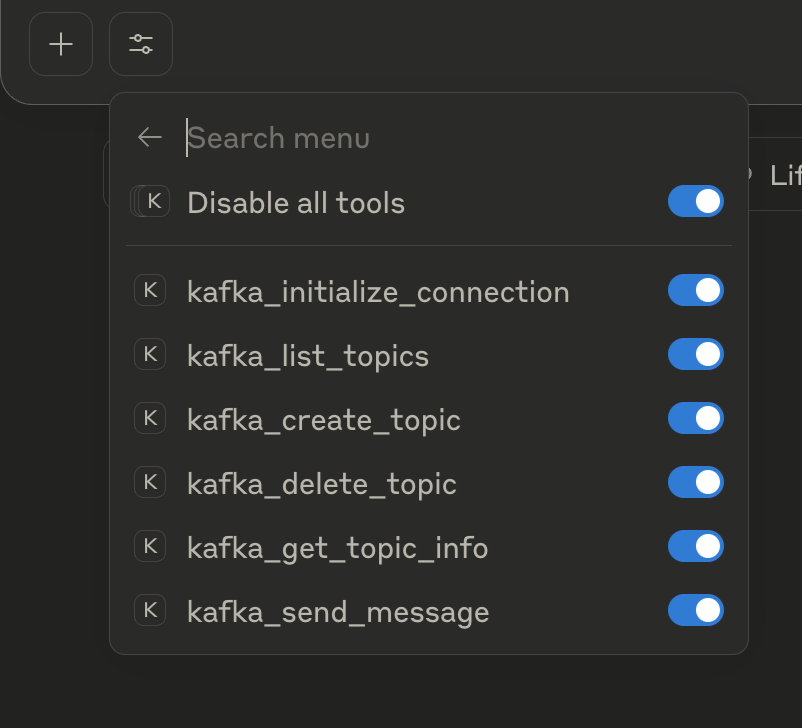
2. Connecting to the Kafka cluster
3. Listing topics
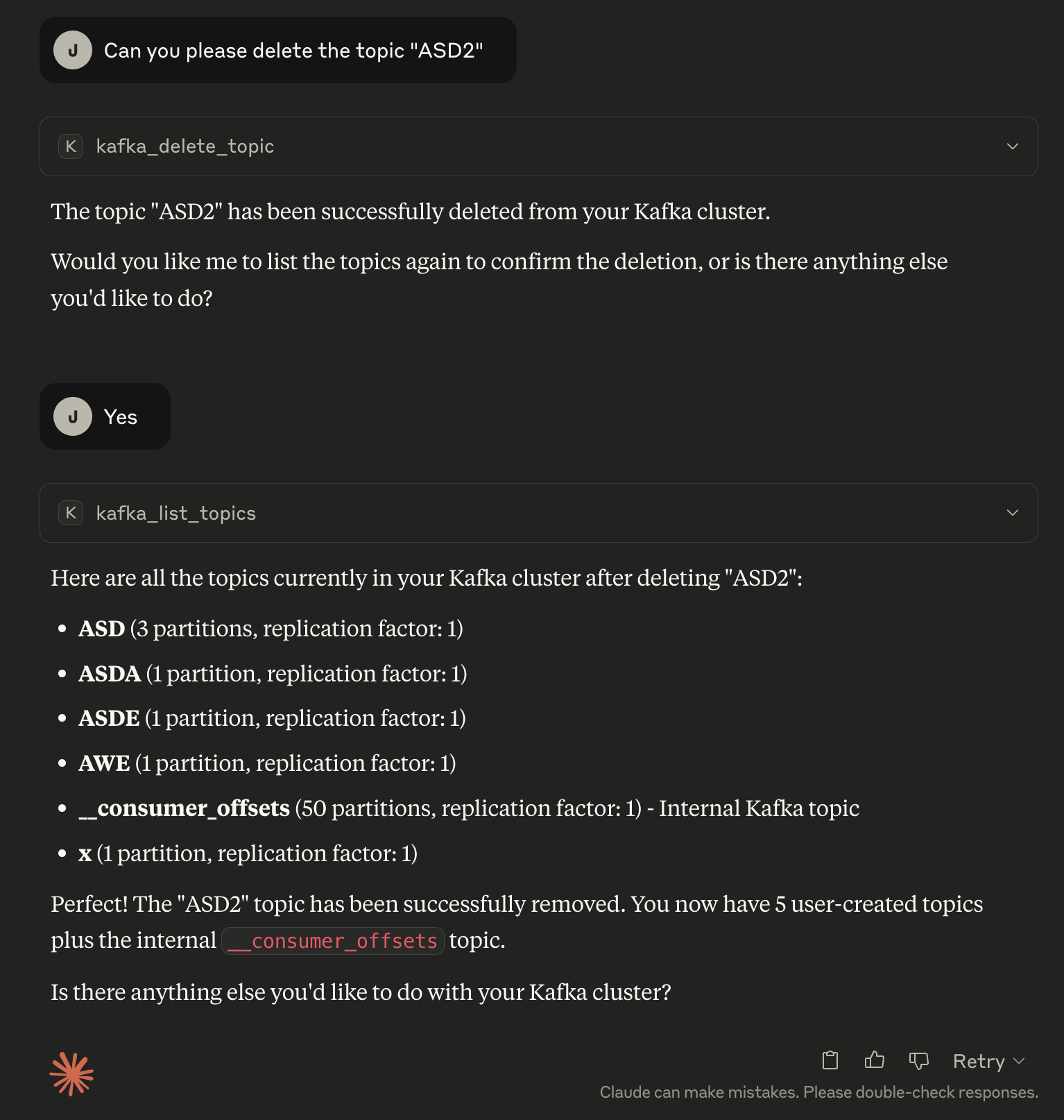
4. Deleting a topic
5. Detailed topic information
6. Producing messages
7. Consuming messages via shell

Final Thoughts
You’ve just transformed your Kafka cluster into a first‑class, LLM‑driven API—ideal for internal dev‑tools, rapid troubleshooting, or even exposing safe, controlled access to non‑Kafka experts. Next up:
- Schema Registry & Avro/JSON serialization
- Consumer group and offset‑management tools
- Cluster‑wide metrics & health checks
- ACLs, security hardening, and multi‑tenant isolation
Feel free to fork, extend, and contribute back at https://github.com/Joel-hanson/kafka-mcp-server. Happy building!
For more Kafka Connect tips and open-source tools, follow the blog series For more on MCP and LLM integration, check out the MCP documentation